Return to Human Cloning Home Page
How is a human being cloned?
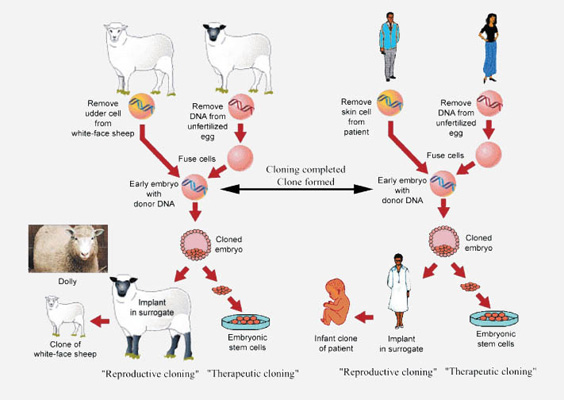
Human beings are cloned through asexual reproduction. Currently, the main process of asexual reproduction used is somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT).
What is asexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction (SCNT) is the reproductive process by which a living being is created that is virtually identical to an existing or previously existing living being. Asexual reproduction does not involve the union of sperm and egg (as this would be sexual reproduction); rather, asexual reproduction yields an exact replica of an already existing animal or human by fusing an egg and a cell nucleus from the person or animal to be cloned.1
 |
| From Cloning |
Have animals been created and birthed using asexual reproduction?
Yes. Dolly the sheep was the first animal successfully cloned. Dolly was created through asexual reproduction and was born in 1996. Since then, numerous species of animals have been cloned. In fact, Texas A&M University has become a leading institution in the field, successfully birthing cloned cattle, goats, pigs, and a cat. 2
Animal cloning is a lucrative business. Genetic Savings and Clone in California will bank genes from a favorite living or deceased pet and clone that pet for a fee. A North Texas woman recently paid $50,000 to have a deceased pet cat replicated; her cat was successfully cloned, using asexual reproduction, and born in Austin on December 10, 2004.3
A human cloning ban does not, of course, ban the cloning of animals. Yet the process by which animals are cloned is the same process by which cloned human embryos are created, thereby presupposing that the recent successful cloning of human embryos, in the exact same manner that animal embryos were cloned and implanted in the womb, is the first step in the successful birth of a human clone.
 |
| From Cloning |
Does human asexual reproduction create a human being?
Yes. Just as the asexual reproduction of a sheep creates a cloned sheep, human asexual reproduction (SCNT) creates a cloned human.4 The cloned human embryo has complete DNA at the single cell stage and, unless prevented from doing so, will continue through the subsequent stages of human development in the laboratory. If implanted in the uterus of a woman, a cloned human baby could be birthed (just as with cloned animals). This cloned human embryo does not merely have the potential to become a life or become a human being. He or she is already a tiny living human being in the embyronic stage with specific gender determined at the single cell stage.
Are scientists currently creating cloned humans?
Yes. Korean scientists at Seoul University made history in 2004 as the first researchers to clone a human being. They removed the nuclei from 242 donated eggs (from 14 women) and fused somatic cells with the eggs to yield 30 cloned embryos.5 The human embryos were cultivated for 5 to 6 days and then destroyed in the process of stem cell extraction; stem cells were successfully harvested from only one of the embryos. No cures for disease, health care benefits, or symptom relief was realized, while 242 human lives were created and sacrificed in the name of research.
 |
| From Cloning |
Scientists at academic institutions in the United States , such as the University of Wisconsin and Harvard, and researchers at private companies, such as Advanced Cell Technology and Geron, have publicly announced efforts to clone human embryos.
1. http://www.encyclopedia.com/topic/clone.aspx
2. Quammen, David. “Clone Your Troubles Away: Dreaming at the frontiers of animal husbandry.” Harpers Magazine, February 2005: 33-43.
3. Nelson, Colleen McCain. “Cloned cat sold to woman for $50,000.” Dallas Morning News, December 22, 2004 .
4. “British Government Grants Human Cloning License for Embryonic Stem Cell Research to Scientist Who Created Cloned Sheep” http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/19882.php. February 10, 2005 .
5. Kolata, Gina. “Scientist Create Human Embryos Through Cloning.” New York Times, February 11, 2004 .


